There is a lot of misunderstanding regarding offshore recruitment and outsourcing. While both systems are built on improving efficiencies and lowering costs, they are completely different services: one focuses on who does the work, and the other on where it’s done.
In a non-political environment, outsourcing is the process of hiring a third-party company to do a specific task. Offshoring is strictly based on hiring people from a different country.
Let’s explain each of them in detail so by the end of this article, you’ll know which hiring method suits you best.
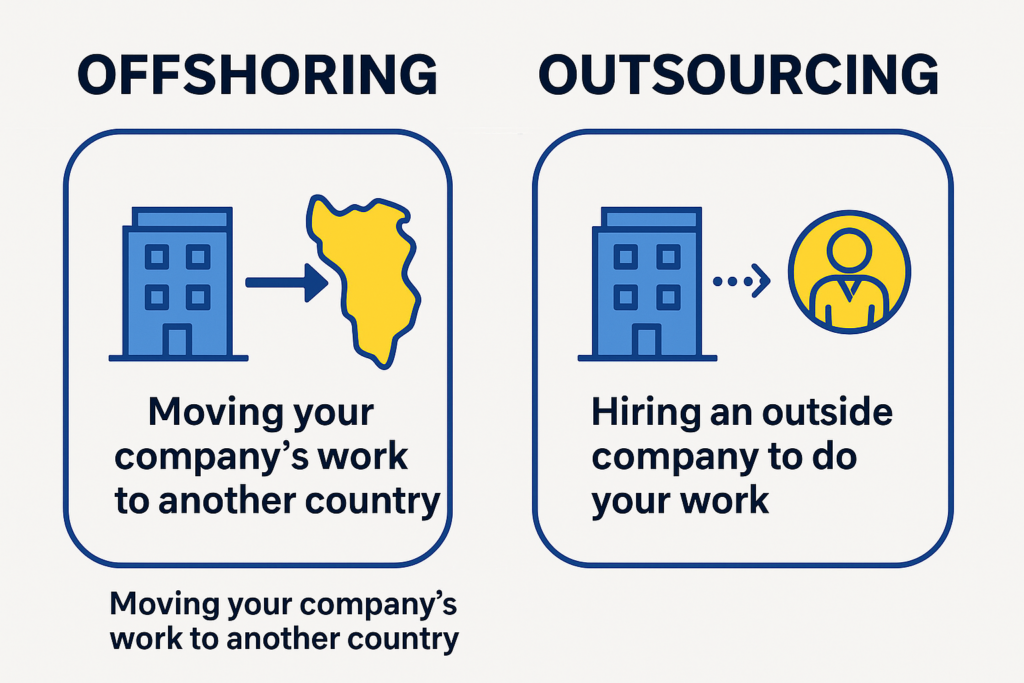
What is Offshoring?
Offshoring means moving your operations to a different country. This means that you are still the owner and controller of your business, but you just do it somewhere else. This can be opening your company’s call center in a different country, opening a development office, or even just hiring individuals from a different country. The common motive is to take advantage of a lower cost, and sometimes stronger, labor market.
Offshore example
A tech company located in the United States opens a development center in India. This allows the company to access more talent and save money because it can pay Indian software developers lower wages than US-based ones. The Indian employees would be considered an extension of that company and be part of its operation.
What is Outsourcing?
Outsourcing is handing over the work to an external company. The company you hire is the owner and controller of that delivery process. The company can be in your country or any other country.
Outsourcing claims to save money by outsourcing work to people with lower salaries. It also offers to remove all your hiring effort, saving your company time and space and allowing to focus on its core capabilities.
Outsourcing Example
For example, a US-based company might outsource its customer support service to a call center that could operate in its region, or it might choose to outsource it to the Philippines, one of the most popular call center countries in the world. A company can also hire an external accounting company to do its accounting or hire a factory to produce its products. The common denominator in all of these options is that an external company is responsible for carrying out the work.
The Core Difference: Offshore vs Outsource
The difference between offshoring and outsourcing is that offshoring moves your in-house operations to another country, while outsourcing hires an external company, anywhere, to handle the work.
Here’s a table to showcase how they differ:
| Feature | Offshoring | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving your operations abroad | Hiring an external company to do the work |
| Location | Always in a foreign country | Can be local or global |
| Ownership | You control the team | The vendor controls delivery |
| Setup Cost | High upfront, lower ongoing | Low upfront, vendor-based fees |
| Duration | Long-term strategic move | Often project-based |
| Risk | Political, compliance, and management complexity | Vendor dependence, less oversight |
✅ Summary: Offshoring = you own the team, abroad. Outsourcing = you hire someone else, anywhere.
Pros and Cons of Offshoring and Outsourcing
Both offshoring and outsourcing offer significant benefits, but each also comes with challenges and risks:
| Model | Main Pros | Main Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Offshoring | • Significant labor & operating cost savings• Access to large, specialized global talent pools• 24/7 “follow-the-sun” support and easy team scaling• Local presence that helps enter new markets | • Time-zone, language, and cultural barriers hamper communication• Harder quality oversight; travel costs for supervision• Exposure to foreign political, legal, and infrastructure risks• Possible backlash at home over exporting jobs |
| Outsourcing | • Lets staff focus on core business while experts handle non-core tasks• Instant access to vendor’s niche skills and technology• Converts fixed costs to flexible, pay-as-you-go fees• Rapidly scale services up or down to match demand | • Less direct control over day-to-day work and quality• Dependence on vendor performance and pricing• Misalignment or communication gaps with an external team• Hidden charges or change fees can erode expected savings |
Offshoring Advantages
1. Significantly Reduces Costs
Most offshoring destinations offer much lower labor and infrastructure costs compared to North American standards. Whether it be economically challenged countries or emerging markets in Europe or South America, India, the Philippines, and so forth, all these offshore countries offer much lower standard of living costs and therefore wages. Companies can therefore benefit by hiring or engaging services offshore significantly reducing their costs.
As an example, one major software company chose to hire software engineers from Bulgaria in Eastern Europe, because of the substantially lower labor costs compared to the average wages paid to software engineers based in California.
2. Access International Talent Not Available Locally
Occasionally local areas won’t provide the necessary pool of talent or professionals with the required expertise. While the lack of skilled workers may persist in the local area, searching offshore countries will likely result in an abundance of candidates with the right credentials ready to work immediately. This gives companies the great advantage of accessing and choosing from a highly skilled workforce.
As another example, we can look to the U.S. government, deciding to hire security professionals in the Middle East, not only for their expertise in the local security issues and environment but also for its cost-effective solution.
3. Access to Favorable Business Environments
Many companies outsource to offshore locations to also take advantage of their favorable business regulations and/or taxation practices. They may be more investor-friendly, more lenient when it comes to labor policies, or in general offer less taxing conditions.
Examples of such up-and-coming offshore locations include Singapore, a very business friendly destination with a growing number of companies setting up shop, as well as Dubai and other destinations offering their business friendly regulations.
Advantages of the Outsourcing Model
1. Frees Up Resources and Capital
When companies transfer their non-core activities to a third party, they free up valuable resources and capital. This capital can then be used for something more critical and/or urgent.
For example, in the situation described above, Apple has more to focus on the color of the flowers at its head office. By hiring gardeners based in Seattle, Apple can free up resources to focus on making better gadgets and computers.
2. Offers Access to Third Party Services and Products
No company can sustain itself by doing everything on its own. It will at some point in time need to seek the services of third party vendors. B2B transactions can also be viewed as outsourcing if the client company seeks services or products on an ongoing basis.
For example, Ford does not have the time nor the resources to maintain a customer care unit in its Michigan office. Thus, it decides to hire professional agencies that can efficiently offer customer care services to their customers. In this case, an Iowa company answers calls and addresses concerns of Ford car owners on behalf of Ford, for which in turn it receives compensation for its services.
3. Affords Companies the Possibility to Focus on Core Competencies
One of the main reasons companies outsource projects is to focus on other more pressing core competencies. It is simply not possible to build on one’s strengths when there are multiple projects requiring your attention.
Oracle hired a third party to do the purchasing homework and assess which computers and laptops were best suited for its productive employees. This way Oracle workers concentrate on its core competencies: developing and maintaining great software programs.
How to Choose Between Offshoring and Outsourcing
Choosing between outsourcing and offshoring talent depends on your goal.
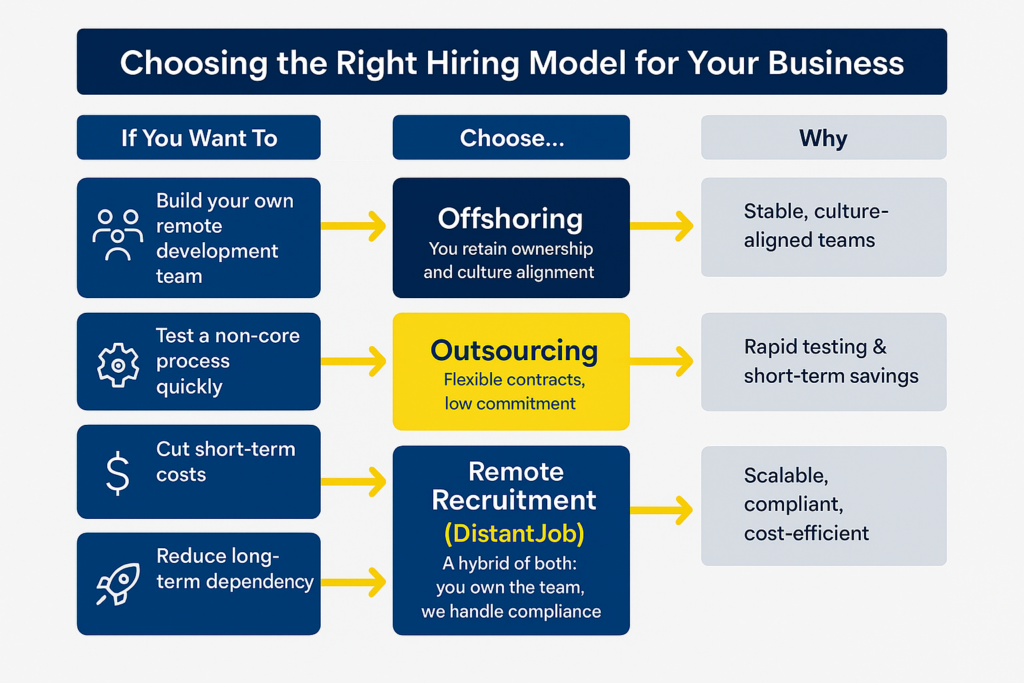
If you want to establish your own remote programming operation, offshoring is hands down the better solution. Offshoring provides you with complete ownership and control of running your company and your culture across borders.
If you prefer to implement a process quickly that is not core to your business, or if you have a need to cut costs immediately, outsourcing will give you more flexibility, because you can set up short-term agreements and avoid setup processes. If eliminating long-term dependency is the priority, then offshoring is also the smarter solution, because you are the owner of your own operation.
And yet, if your goal is to safely open your programming operation in a way that limits the complex legal and administrative issues of a traditional offshore approach, a remote recruitment company like DistantJob is the smarter, modern alternative. You will be the owner of your product, but we will handle the payroll, compliance, and HR issues.
Both traditional offshoring and outsourcing have trade-offs and remote recruitment bridges that bridge the gap.
Conclusion
Now that we’ve got the jargon right, know that offshoring and outsourcing are tools, not opposites. The right model depends on your goals:
- If you want long-term control — go offshore.
- If you want flexibility — outsource.
- If you want both, choose remote recruitment & staffing services.
Try before you commit. DistantJob’s staffing model lets you add vetted remote developers to your team on a monthly basis. No upfront recruitment fees, no long-term lock-in — just skilled engineers ready to ship code, with the option to convert to full-time when you’re ready. DistantJob helps companies hire vetted global developers quickly, giving you full control over your team without the complexity of offshoring.
What is the difference between offshore and outsourcing?
Outsourcing focuses on who does the work (external vendor), while offshoring focuses on where the work happens (foreign country).
IT companies often prefer offshoring or remote recruitment to retain IP control and build long-term technical expertise.
No. Remote hiring allows you to directly employ global talent without creating a foreign subsidiary — it’s offshoring without the overhead.
Legal compliance, cultural gaps, time-zone challenges, and political stability in the host country.





